Lung Cancer CT Scan: Essential Insights for Early Detection
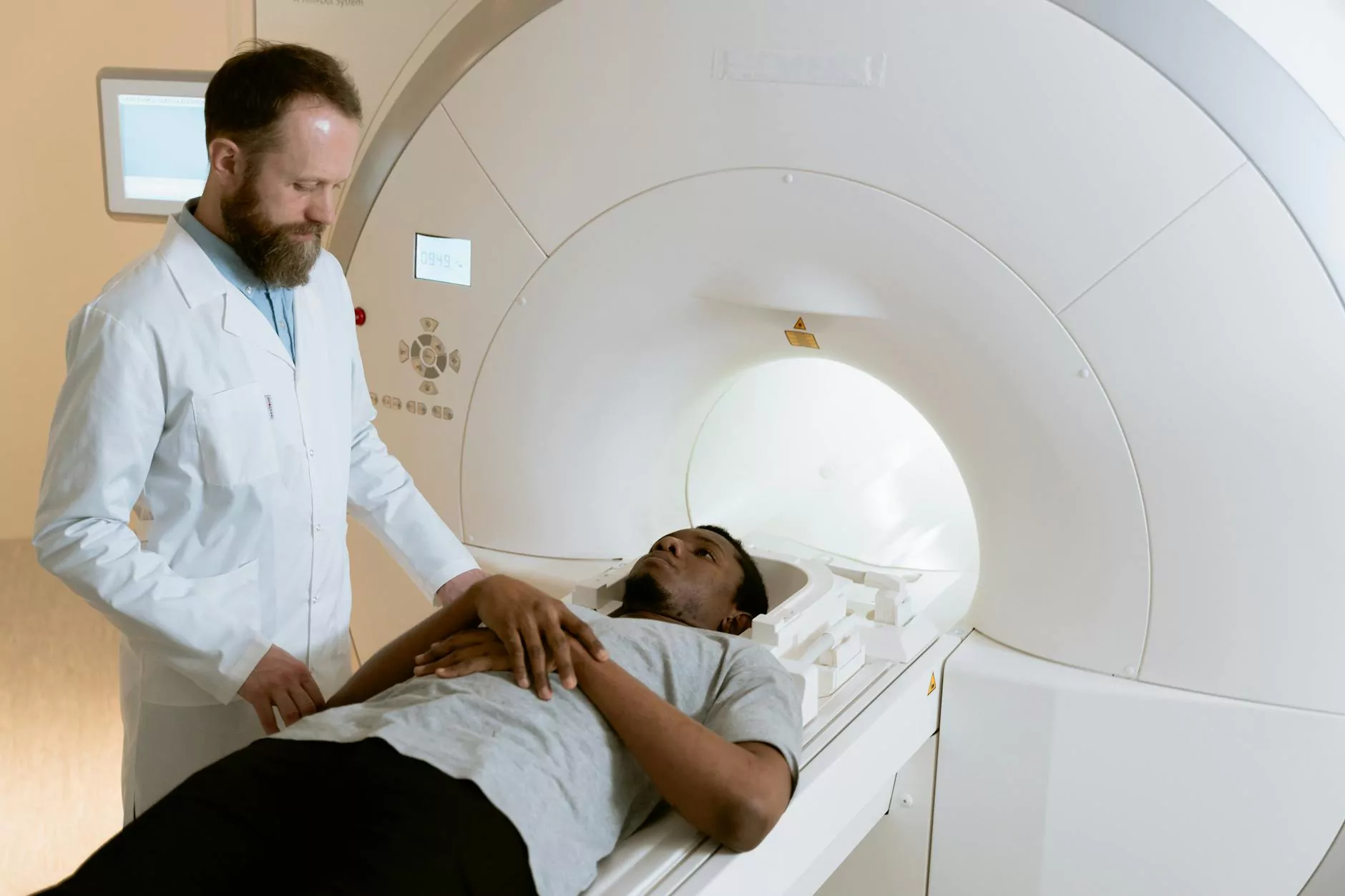
Lung cancer remains one of the most prevalent and deadly forms of cancer worldwide. Early detection is crucial for improving patient outcomes, and advanced imaging techniques, especially the lung cancer CT scan, play a pivotal role in this process. This article delves into the specifics of lung cancer detection, the significance of CT scans, and how this technology is reshaping healthcare protocols.
Understanding Lung Cancer
Lung cancer primarily develops in two main forms: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Understanding the nuances between these types, alongside their risk factors, can greatly assist in early identification. Key risk factors include:
- Smoking: This is the most significant risk factor, accounting for a majority of lung cancer cases.
- Exposure to secondhand smoke: Non-smokers exposed to smoking environments have an increased risk.
- Environmental toxins: Long-term exposure to substances like asbestos, radon, and other carcinogens can heighten risk.
- Family history: A genetic predisposition can play a role in one's likelihood of developing lung cancer.
- Chronic lung diseases: Conditions such as COPD may increase lung cancer risk.
What is a Lung Cancer CT Scan?
A lung cancer CT scan, also known as a computed tomography scan, is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the lungs. Unlike traditional X-rays, CT scans offer a much clearer and more detailed view of lung structures, making them invaluable in lung cancer detection and diagnosis.
How Does a Lung Cancer CT Scan Work?
The process involves a sophisticated machine that takes numerous X-ray images from different angles. These images are processed by a computer to produce detailed pictures of the lung tissues, allowing healthcare professionals to:
- Detect tumors: CT scans can reveal smaller tumors that may be missed on standard X-rays.
- Assess tumor size and location: Accurate information about the tumor helps in determining the best treatment approach.
- Guide biopsies: In some cases, CT scans are used to guide needle biopsies, ensuring that samples are taken from the correct location.
Why is Early Detection Important?
The prognosis for lung cancer is significantly better when detected early. According to the American Cancer Society, the 5-year survival rate for localized lung cancer is about 61%, compared to only 4% for distant-stage lung cancer. Key reasons for prioritizing early detection include:
- Increased Treatment Options: Early detection can open the door to a wider range of treatment options, including surgical removal of tumors before they spread.
- Improved Survival Rates: Early-stage lung cancer has a significantly higher chance of being successfully treated.
- Reduced Treatment Costs: Treating cancer at a less advanced stage often incurs lower costs and less intensive treatment regimens.
The Process of a Lung Cancer CT Scan
What to Expect During the Procedure
When undergoing a lung cancer CT scan, patients can expect the following steps:
- Preparation: Patients might be instructed to avoid eating or drinking for a few hours before the scan.
- Positioning: Patients are asked to lie on a padded table, which slides into the CT scanner.
- Imaging: The technician will operate the machine and may ask patients to hold their breath temporarily for clearer images.
- Contrast Materials: In some cases, contrast dye may be injected to enhance image clarity.
- Duration: The scan itself typically lasts 10 to 30 minutes.
After the CT Scan
Once the scan is complete, the technician will review the images. A radiologist will interpret the scans and send a report to the patient's physician, who will discuss the results and possible next steps.
Types of Lung Cancer CT Scans
There are various types of CT scans utilized in lung cancer detection:
- Standard CT scans: Provide detailed images of the lungs and surrounding tissues.
- High-resolution CT scans: Offer even clearer images, essential for assessing the lung structure and detecting smaller lesions.
- CT pulmonary angiography: Used to examine the blood vessels in the lungs and identify any potential clots or abnormalities.
Benefits of Lung Cancer CT Scans
Lung cancer CT scans provide numerous advantages, including:
- Enhanced Accuracy: Provide precise images that can reveal nodules and other abnormalities that are not apparent through standard imaging.
- Non-invasive: The procedure is quick and does not require any surgical intervention.
- Monitoring: CT scans can be used for ongoing monitoring of patients with a history of lung cancer, ensuring timely interventions if new issues arise.
Risks and Considerations
While lung cancer CT scans are generally safe, it is essential to consider potential risks:
- Radiation Exposure: Although the dose is relatively low, repeated exposure could pose a risk.
- False Positives: Occasionally, benign nodules may be misinterpreted as cancerous, leading to unnecessary stress and additional testing.
Conclusion
In the battle against lung cancer, early detection through advanced imaging techniques like the lung cancer CT scan is pivotal. Understanding the process, benefits, and considerations helps patients make informed decisions regarding their health. If you or a loved one is at risk, consult a healthcare professional to discuss the necessity of a CT scan and other appropriate screening options.
At Hello Physio, we specialize in providing comprehensive Health & Medical, Sports Medicine, and Physical Therapy services to our clients. We are committed to improving client health through effective assessment and tailored treatment plans.









